

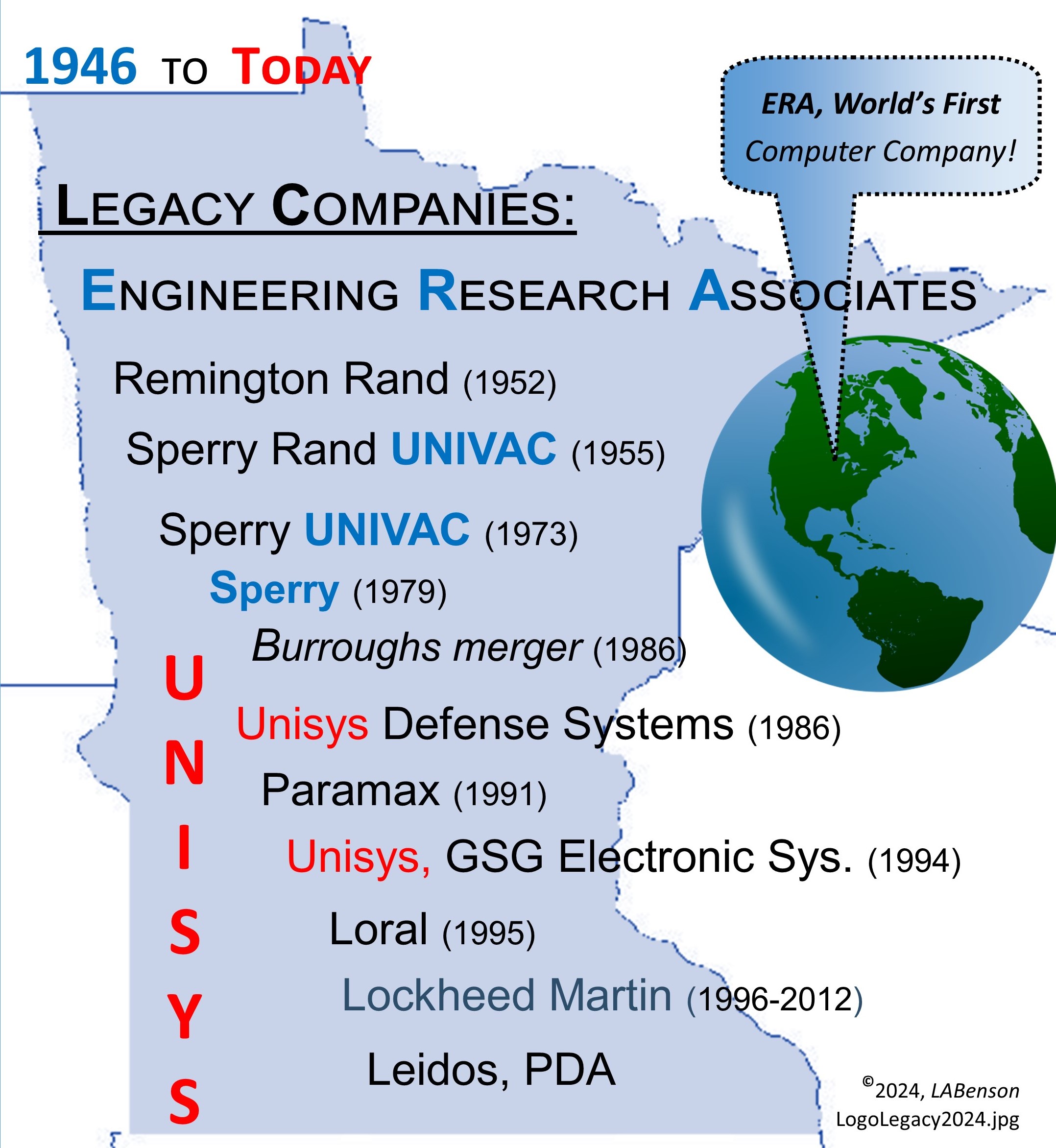
Information Technology (IT) Pioneers
Retirees and former employees of Unisys, Lockheed Martin, and their heritage companies
Milestones, Chapter 5
ERA, Minnesota's Technology Wellspring.
 This website and our Legacy initiative are not trying to re-write
history! Rather, we are clarifying what a small company named ERA in
St. Paul, Minnesota started and what our engineering prowess has continued
doing under various corporate names for over seven decades. Many
employees, after experiencing ERA/UNIVAC developments, left to form
other technology driven companies - see the Spinoffs chapter!
This website and our Legacy initiative are not trying to re-write
history! Rather, we are clarifying what a small company named ERA in
St. Paul, Minnesota started and what our engineering prowess has continued
doing under various corporate names for over seven decades. Many
employees, after experiencing ERA/UNIVAC developments, left to form
other technology driven companies - see the Spinoffs chapter!
These achievements have been mostly overlooked by the academic community as they were documenting computer history. Two reasons:
- Defense industry projects, sometimes classified, get very little exposure to anyone other than the military, and
- Technology forums held by the defense industry for information exchanges with the various military branches usually were not opened to students or professors.
This chapter lists major achievements; our engineering, computer, and systems chapters have stories about these and other significant events. Thanks to Quint Heckert and others for the information. [lab]
Accomplishments to Note!
1945!!! Financier John Parker met with Admiral Nimitz. ERA incorporation papers were filed with the State of Minnesota on December 27th. The papers were accepted in January, 1946. This data was found by Legacy committee member Quint Heckert while supporting our 2008 Sesquicentennial initiative.
 1946:
On January 8th ERA opened their doors for business and began development
of magnetic storage drums on 'classified' contracts. These were the
'grandmothers' of today's rotating storage devices, such as the hard
drives in today's PCs and the floppy disks used with PCs during the
80s and 90s. The prototype drum is in the Minnesota Historical Society
center.
Engineering Memory Chapter (vipclubmn.org)
1946:
On January 8th ERA opened their doors for business and began development
of magnetic storage drums on 'classified' contracts. These were the
'grandmothers' of today's rotating storage devices, such as the hard
drives in today's PCs and the floppy disks used with PCs during the
80s and 90s. The prototype drum is in the Minnesota Historical Society
center.
Engineering Memory Chapter (vipclubmn.org)
1947: ERA delivered the Goldberg I with a drum memory for a U.S. Navy crypto-analytic system. Goldberg I and II were developed for the Navy, for classified purposes. They are historically significant as the first magnetic drum was built for use with Goldberg I. The drum was a 34 inch drum with magnetic tape bonded to the drum surface to provide a recording medium. The drum advanced slowly, 1 row at a time for writing, but was run at 50 rpm for reading. Goldberg II was not delivered until 1951 due to being out-prioritized by the requirement to deliver the DEMON machines. [reference page 31 of the 1947 to 1959 Remington Rand UNIVAC Product book, .]
1948: Delivered the Demon I and II 'Analytic Machines' to be used for cryptography work by the U.S. Government, 24-bit Computer Chapter (vipclubmn.org). These 24-bit machines were programmed with plug boards while using the drums for data storage and manipulation. These drum memories were the world's first delivered, operational hard drives. This was also a 34 inch drum, but rotated at 240 rpm, equivalent to a data transmission rate of 20,000 pulses per second. Five DEMONS were delivered in Oct. 1948. [Norberg's book, page 63.]
1950: Shipped the ATLAS computer
to Central Intelligency Agency's predecessor via railway car in October 1950. This computer
is believed to be the world's first stored program computer installed
for operations at a customer's site in December 1950. The site and application
were classified until 1977 thus didn't appear in any early computer
technology books.
{Editor's notes: Yes, there were a couple of laboratory stored program
computer concept demonstrations before this delivery, however their
memory sections used various storage tube hardware that lost both data
and programs when power was interrupted - necessitating a 're-boot'
quite often. The ATLAS, a drum based system kept the data and programs
when power was off thus could easily resume operations.
ERA's then president, John Parker, got government permission to build
and market a commercial version of this Atlas computer. Since the Atlas
was designed and built under Task 13, Jack Hill, a versatile ERA engineer
suggested that the commercial version be numbered the 1101, which is
13 in binary. Subsequent copies transitioned from ERA 1101, ERA 1102,
ERA 1103, UNIVAC 1103, UNIVAC 1103A (UNIVAC Scientific), etc. The series
is then had the UNIVAC 1105, 1107, 1108, Sperry 1106, 1110, UNISYS 1110,
Unisys 2200, ... continuing in production to 2008.}[lab]
1951: ERA delivered the Goldberg II crypto-analytic system to the U.S. Navy; This system used photo-electric sensing and paper tape scanning to achieve high input rates. {Editor's Note: EMCC in Philadelphia delivered the first UNIVAC I to the U.S. Census Bureau. This was the first commercial digital computer in the world utilizing stored programs. Copied from a 'Calendar of UNIVAC Technology', two sheets circa 1981.}
![]() 1952:
1952:
- Delivered the UNIVAC Scientific Model 1102 to Arnold Research Center in Alabama; the first on-line scientific computer based on the then classified ATLAS II, ERA1102.pdf (vipclubmn.org).
- Delivered the Automatic Antenna Coupler, an impedance matching device which enabled efficient long range oceanic radio communications for aircraft, Engineering, Antenna Coupler Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
- Delivered a paper design of a Drum Memory computer to several IBM laboratories. When IBM announced their impending model 650 in 1953, it included a drum memory from a vague patent licensing agreement with ERA. Engineer John Coombs, was on the 650 develompment team - hired by IBM from ERA.
1953:
- In October of '53 the first ATLAS II was delivered to the National Security Agency (non-classified nomenclature was 1103.) See page 13 of History of NSA General-Purpose Electronic Digital Computers (vipclubmn.org).
- Completed the UNIVAC Flight Plan Storage System for automatically accepting, storing, and delivering flight plans and weather information, see the Air Traffic Control Chapter for the rest of this topic.
- ERA Speed Tally System installed at John Plain and Company of Chicago - Project Engineer was Don Weidenbach. See page 51 of UNIVAC1959Products.pdf (vipclubmn.org).
1955:
- Developed the core memory for the UNIVAC II S/N 0 in the Minnehaha facility. {Editor's note: Philadelphia developed the UNIVAC II providing flexibility of instruction repertoire with the attachment of a magnetic core memory. Copied from a 'Calendar of UNIVAC Technology', two sheets circa 1981.}
- UNIVAC File Computer Model 7 Developed, combining commercial data processing with large storage capacity and rapid access.
-
 US Navy, Bureau of Ships
contracts with Remington Rand UNIVAC
for the Naval Tactical Data System (NTDS). This contract was for
the AN/USQ-17 unit computer, militarized magnetic tape units, paper
tape reader/punch, computer control panel, modified teletype units
for communication with non-NTDS ships, prototype automatic radar
video processor, and software.
US Navy, Bureau of Ships
contracts with Remington Rand UNIVAC
for the Naval Tactical Data System (NTDS). This contract was for
the AN/USQ-17 unit computer, militarized magnetic tape units, paper
tape reader/punch, computer control panel, modified teletype units
for communication with non-NTDS ships, prototype automatic radar
video processor, and software.
1956: Delivered the world's first airborne digital computer, UnivacComputersI'veKnown.pdf (vipclubmn.org).
![]() 1957:
Delivered the second Bomarc Guidance
Computer for the Titan Missile System,
1104 Computer
Application (vipclubmn.org).
1957:
Delivered the second Bomarc Guidance
Computer for the Titan Missile System,
1104 Computer
Application (vipclubmn.org).
1958:
- Delivered the first Naval Tactical Data System (NTDS) AN/USQ-17 computer to counter the power of a growing airborne threat to the U.S. fleet. This system included advanced digital techniques, Systems, Navy Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
- Delivered the ERA 1103 S/N 4 computer to the University of Minnesota, the beginning of their Computer Science Department in the school of Electrical Engineering, this machine had been in use before.
1959:
- Delivered the UNIVAC SCIENTIFIC Model 1105, a high-speed digital computer with great programming versatility and large internal external storage capacity.
- Delivered the first Athena missile launch computer to the USAF, initially a ground based guidance computer for the TITAN I intercontinental ballistic missile system. Athena plus associated UNIVAC developed software are credited with over 300 successful launches from the Cape and Vandenberg Air Force Base.
- Delivered the Target Intercept Computer for the Nike Zeus anti-missile system.
- Delivered the AN/USQ-20 systems for NTDS service test at NEL, and eventually in the USS ships King, Mahan, and Oriskany.
- Published a St. Paul capabilities booklet that described many of the products delivered to date, BitsBakUp/U2857%20UNIVAC%20St.%20Paul%20Capabilities%20Brochure%20(1960).pdf
1961:
- AN/USQ-20 computer installed in the USS BAYA (AGSS-318). First installation of an AN/USQ-20 aboard a US Submarine. Computer was used as an integral part of LORAD. {Lowell's note: In a conversation with Dick Erdrich in 2025, The CP642A core of the USQ-20 system did not fit through the submarine hatches so they just took the electronic drawers below deck and had to rig up a special backpanel to interconnect them. It worked!)
- UNIVAC ADD-1 Aerospace Computer announced. This was the compact completely solid state airborne computer capable of computations previously available in large scale ground based computer installations.
- NTDS demonstrated on the USS Enterprise carrier in November! (Systems, Navy Chapter (vipclubmn.org))
1962:
- Delivered the first of 38 1107 commercial computer systems.
- NTDS approved for installation in first Nuclear Powered Naval Ships, USS Long Beach, CGN-9 and USS Enterprise, CVA-65.
- First operational 'Hands Off' - arrested carrier landing using the AN/SPN-42 system with the type 1218 computer. {The last AN/SPN-42 system was shut off in 2015!}
1963:
- Delivered the first of 239 NTDS standard computers (CP-642B(type 1212)) including Thin Film Memory for index registers and I/O buffer control words..
- Delivered the first of 326 type 1218 computers (CP-789) for shipboard as well as ATC ARTS I systems.
- Delivered the ADD 1020 (CP-754/A) to the Navy as the first airborne Anti-Submarine Warfare computer, entry #2 of OceanSurveillance.pdf (vipclubmn.org).
- Tested the Navy's TRANSIT system, the first government use of a GPS system, Systems, Navy Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
1964:
- Delivered the first type 1824 missile borne solid state guidance computer, 24-bit Computer Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
- Delivered the first CP-667 ruggedized 36-bit shipboard computer, 36-bit Computer Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
- Delivered the first CP-808, for the Marine Tactical Data System, 30-bit Computer Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
1965:
-
 Delivered
the first of 303 model 1108 commercial computer systems. The last
was delivered in 1975.
Delivered
the first of 303 model 1108 commercial computer systems. The last
was delivered in 1975.
- Delivered the first of 39 real-time computer systems (CP-855/UYK(1230)) for the NASA global tracking and data acquisition network used in Project Apollo.
- Delivered the first of 367 shipboard missile launch computers (CP-848/UYK (1219B))
- Delivered the CP-823/U (1830) to NADC to begin ASW software development.
1967:
-
 Delivered the first CP-901 (1830A) in September for the P3-C
anti-submarine warfare and navigational data system. Two decades
later, the Tom Clancy book and movie, "Hunt for Red October" showed
a P-3C dropping sono-buoys to track the 'Red October'. The CP-901
computer used in this system was still in use at that time, we had
developed the operational software at out Warminster, PA facility.
Several UNIVAC engineers had opportunity to ride on this aircraft
while supporting the system.
Delivered the first CP-901 (1830A) in September for the P3-C
anti-submarine warfare and navigational data system. Two decades
later, the Tom Clancy book and movie, "Hunt for Red October" showed
a P-3C dropping sono-buoys to track the 'Red October'. The CP-901
computer used in this system was still in use at that time, we had
developed the operational software at out Warminster, PA facility.
Several UNIVAC engineers had opportunity to ride on this aircraft
while supporting the system.
In 2012, Bob Pagac, retired LMCO Program Manager noted that there were still 40 CP-901s flying in the Japanese ocean survelliance systems.
S/N 499, the last one, was shipped in 1992 - a 25 year production run! - Delivered the first of 19 CP-808/TYK (1213) computers to the Marine Tactical Data System (MTDS).
- Delivered Exec-8, the multi-processor operating system of the 1108 commercial computer {with various updates, Exec-8 had a 40+ year life.}
1968:
- Delivered the first of 164 CP-890/UYK computers to Sperry Systems Management for submarine applications.
- Delivered the first of 17 1230 MTC computers to the USAF for tracking 'space' junk.
1969:
- Delivered the first of 338 model 1106 commercial computer systems, the last delivered in 1976.
- Delivered the first UNIVAC AN/UYK-7, the standard computer for Command and Control in the United States Navy and ultimately employed in all of the U.S. military services as well as a couple of cooperating NATO Navies. Over 3,000 units built.
- First defense contractor to become a node on the emerging ARPAnet, the predecessor to the internet. Other nodes at the time were government research laboratories and University laboratories.
- Delivered computers used for photo enhancement system in the Mariner 9 Mars space program.
- Delivered the first 1830B computer system to the German Navy for use in their coastal F-143 Fast Patrol Boats.
1971:
- Delivered the Minuteman Weapons Systems computer, the AN/UYK-11. This machine used a specially engineered plated wire memory whose storage characteristics were resistant to nuclear blast effects.
- Delivered the UNIVAC Air Traffic Control System (ARTS III) used to provide new air traffic control safety at the 64 major U.S. airports.
1972:
- Delivered the first of 455 model 1110 commercial computer systems, the last delivery in 1979.
- Delivered the first production unit of the UNIVAC type 1832 computer [nomenclature AN/AYK-10] for the S-3A carrier based anti-submarine warfare jet plane. This machine was a dual processor and dual I/O 32 bit machine with dual memories to facilitate reduced mission objectives should there be a partial failure in any part of the machine. It used the same Instruction Set Architecture as the AN/UYK-7 shipboard computer. We also did the systems programming for this mission computer at our Valencia facility.
- Delivered the first AN/UYK-15 computer to ITT Gilfillan for a US Navy submarine application.
- Buillt a very early 8-bit Micro Computer System,
UnivacMicro.pdf (vipclubmn.org).
1973:
- Completed MIL-E-5400 testing then delivered the first of 93 AN/UYK-23 (1816) computers to several customers, 16-bit Computers (vipclubmn.org).
- Delivered the 1819 Avionics Computer to Sperry Flight Systems.
![]() 1974:
Delivered the first UNIVAC AN/UYK-20, the U.S. Navy standard
small to medium scale computer for tactical operations.
1974:
Delivered the first UNIVAC AN/UYK-20, the U.S. Navy standard
small to medium scale computer for tactical operations.
1975:
- Developed the Communication and Display subsystem (CADS), a dual-screen, high-performance display for intelligence applications.
- Delivered the first model 1100/10, /20, & /30 commercial computer systems, the last of 359 in 1980.
1976:
- Developed the world's first point-to-point fiber optic digital interconnect system.
- Delivered the first model 1100/80 commercial computer systems, the last of 1121 in 1985.
1977: Former ERA engineer/manager Erwin Tomash and wife Adele found the International Charles Babbage Society, renamed the Charles Babbage Institute (CBI) in 1979 and then moved to the University of Minnesota in 1980. With support from industry and individuals, the University established the 'Engineering Research Associates Land-Grant Chair in the History of Technology' in 1989, initially held by CBI Director Arthur Norberg. Under Norberg's leadership, CBI developed into the world's leading research center for the history of information technology. The field's leading journal, ANNALS OF THE HISTORY OF COMPUTING, is being edited by CBI staff (2008-12) [Dr. Tom Misa]
1978: Delivered the 100th Minuteman III Weapons System Controller, the 500th AN/UYK-7 Computer, and the 1,000th AN/UYK-20 Computer.
![]() 1979:
1979:
- Delivered the AN/UYK-502 computer, one of the most adaptable, flexible mini-computers offered in a MIL-SPEC design to the Canadian Navy. This machine had software compatibility with the AN/UYK-20. We subsequently transitioned production of this machine to a Winnipeg facility.
- Delivered the AN/AYK-15A (type 1625) to the Air Force Avionics Laboratory. This jet fighter environment ready airborne computer was one of the first to implement the AF's new MIL-STD-1750 Instruction Set Architecture. This used a USAF supplied Jovial compiler for developing operational software.
- Delivered the first model 1100/60, /70 commercial computers, the last of 2,863 in 1988.
-
 Sperry formed the VIP Club
as a retirees social and service organization
with a meeting room in Plant 1. The room was opened on July
23 with a formal ceremony - see Club
History for specific Club milestones.
Sperry formed the VIP Club
as a retirees social and service organization
with a meeting room in Plant 1. The room was opened on July
23 with a formal ceremony - see Club
History for specific Club milestones. - Selected to design, develop, and manufacture the AN/UYK-43 computer under a three year contract with the United States Navy. The AN/UYK-43 became the Navy's next generation standard large-scale computer, while using the same Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) as the previous AN/UYK-7, AN/AYK-10, and CP-140 computers, 32-Bit Computer Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
- Chosen to design and develop the AN/UYK-44 computer under a three year contract with the United States Navy. The AN/UYK-44 became the Navy's next generation standard small to medium scale computer using the same ISA as the Type 1616, AN/UYK-15, AN/UYK-20, AN/UYK-23, and U3760 computers, 16-bit Computers (vipclubmn.org).
- Delivered the SPERRY UNIVAC 1655 Dual/Single Screen Color Terminal to Bunker-Ramo for the Air Force Advanced Electronic Warfare Evaluation and Display System (AEWEDS) Program.
1981:
- Delivered the first militarized production fiber optic system used with the Ground Launch Cruise Missile system, Engineering Interfaces Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
- 1st direct, international sale to JMSDF, the P3-C Program Generation Center/Software Development Facility (PGC/SDF) was accepted and turned over to the JMSDF in their new facility located at the Atsugi NAS, located west of Tokyo, Japan.
- Developed VIPS, the first commercial production voice mail system, read about it in Articles/InventionofVoiceMail.pdf.
- Delivered the first model 1100/60, /70 ROED commercial computer systems, the last of 904 systems in 1987.
1982:
- Delivered the 2,000th AN/UYK-20 computer.
- Delivered the first model 1100/70 Dyad commercial computer system, the last of 77 systems in 1987.
![]() 1983:
Delivered the first model 1100/90
commercial computer system, the last of 1,318 systems in 1989.
1983:
Delivered the first model 1100/90
commercial computer system, the last of 1,318 systems in 1989.![]()
1984:
- Delivered an AN/AYK-10 upgrade giving the S-3B ASW aircraft the capability to launch Harpoon missiles at ship or shore targets, 32-Bit Computer Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
- Delivered the first AN/UYK-43 Computer in October, 1984 - AnUyk43Computer.pdf (vipclubmn.org).
- Delivered the first System 11 commercial computer systems, the last of 603 systems in 1988.
1985: Delivered the first model 2200/200 commercial computer system, the last of 966 systems in 1990.
1986:

- Delivered the first mission computer for the Northrop B-2 stealth bomber, B-2StealthBomberStory.pdf (vipclubmn.org).
- Celebrated 40 years since ERA opened their doors with a plaque (Locations Chapters (vipclubmn.org)) and a booklet, ERA40thAnniversary.pdf (vipclubmn.org).
1987:
- Delivered a radiation hardened CMOS 32-bit microprocessor chip set to the CIA as part of their SDI programs, Special Purpose Computers Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
- Delivered the first model 1100/90 Dyad commercial computer systems, the last of 28 systems in 1988.
1988: Delivered the first model 2200/40 and the first model 2200/600 commercial computer systems.
1989: Delivered the first model 2200/100 commercial computer system.
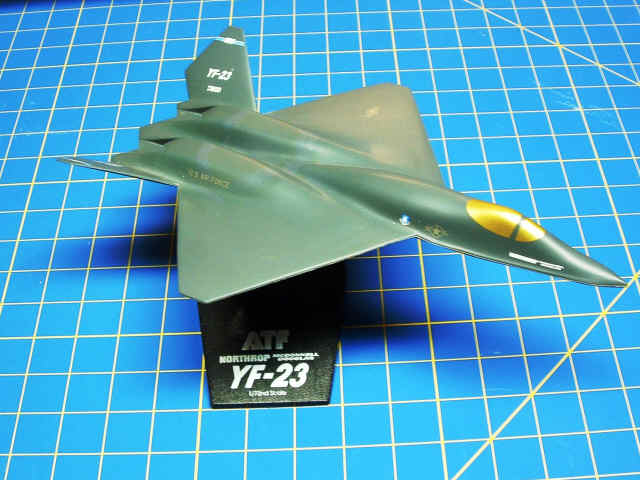 1990: Delivered 'Common Module'
card sets for embedding into the YF-23 stealth aircraft as part of the
Northrop development,
AF Computers
Chapter (vipclubmn.org). Lockheed Martin won the fly-off in 1991 with their
YF-22. This model YF-23 model was given to Lowell's
granddaughter when she was hired by Northrop-Grumman as an
Aero-space systems engineer in 2019.
1990: Delivered 'Common Module'
card sets for embedding into the YF-23 stealth aircraft as part of the
Northrop development,
AF Computers
Chapter (vipclubmn.org). Lockheed Martin won the fly-off in 1991 with their
YF-22. This model YF-23 model was given to Lowell's
granddaughter when she was hired by Northrop-Grumman as an
Aero-space systems engineer in 2019.
![]() 1991:
Developed then delivered the first developed Automated Mail Sorting machines used
by the US Postal service,
Systems,
Government Chapter (vipclubmn.org)
1991:
Developed then delivered the first developed Automated Mail Sorting machines used
by the US Postal service,
Systems,
Government Chapter (vipclubmn.org)
2006: Developed the Integrated Core Processor for the Joint Strike Fighter. A single board had four embedded micro-processor chips, 'Dick' Erdrich was the hardware design architect, Articles/JSF_Eagan.pdf.
2007: The 50th anniversary of shipment of Athena, the first
UNIVAC transistor computer.
The fall of 2007 was the 45th anniversary of the first 1107 shipment to CSC in California.
2010, November: Lockheed Martin announced the closing of the Eagan facility by the end of 2012; thus ending 66 years of IT Technology innovations in the Twin Cities, PLANT8CLOSED.pdf (vipclubmn.org).
2011: S/N 8000 AN/UYQ-70 delivered to the US Navy
in March from the Clearwater FL facility; this was installed into the
USS Minnesota, a new submarine launched in Sept., 2013.![]() See section 6.3 of
Engineering, Peripherals Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
See section 6.3 of
Engineering, Peripherals Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
2012, December: The Legacy's artifact collection was shipped to the Lawshe Museum in South St. Paul to begin exhibiting 66 years of computer innovations, Legacy Exhibits Chapter (vipclubmn.org).
 2016,
September: The Air Traffic Management (Systems, Air Traffic
Control Chapter (vipclubmn.org)) operations
of Lockheed Martin in Eagan, MN were 'spun -off' to become a part of
Leidos corporation. Thanks to Steve Koltes who provided the
logo sequence shown at the right.
2016,
September: The Air Traffic Management (Systems, Air Traffic
Control Chapter (vipclubmn.org)) operations
of Lockheed Martin in Eagan, MN were 'spun -off' to become a part of
Leidos corporation. Thanks to Steve Koltes who provided the
logo sequence shown at the right.
2017, June: The UNISYS, Roseville operations were merged with the UNISYS, Eagan operations - The Shadowboxes with the commercial 1100 systems history was moved to Eagan at this time, Through the Ages Exhibit (vipclubmn.org).
2021, January 8th: Recognized 75 years since ERA's doors opened in St. Paul, MN. - Read about it in Articles/Anthologies2Go.pdf.
2023, March 7th: Celebrated a reopening of the Lawshe Memorial Museum with a dedicated room for photo archiving and revised artifact exhibits in the great room.
2023, June 15th: Unveiling of a commemorative plaque recognizing ERA as the technology beginning in the state of Minnesota, Read Spinoffs, Chapter 6 (vipclubmn.org) and ERA-History_Talk.pdf (vipclubmn.org).